Jump right into our summarized introduction to the basics of SCADA!
From the Start
In the mid-20th century, industrial facilities depended on personnel to physically control and monitor equipment. However, as the industry grew much larger, the innovation for equipment control arose. In the early 1970s, the Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system was invented. The system allowed for automatic control systems to monitor and control equipment and processes.
About this Amazing Software
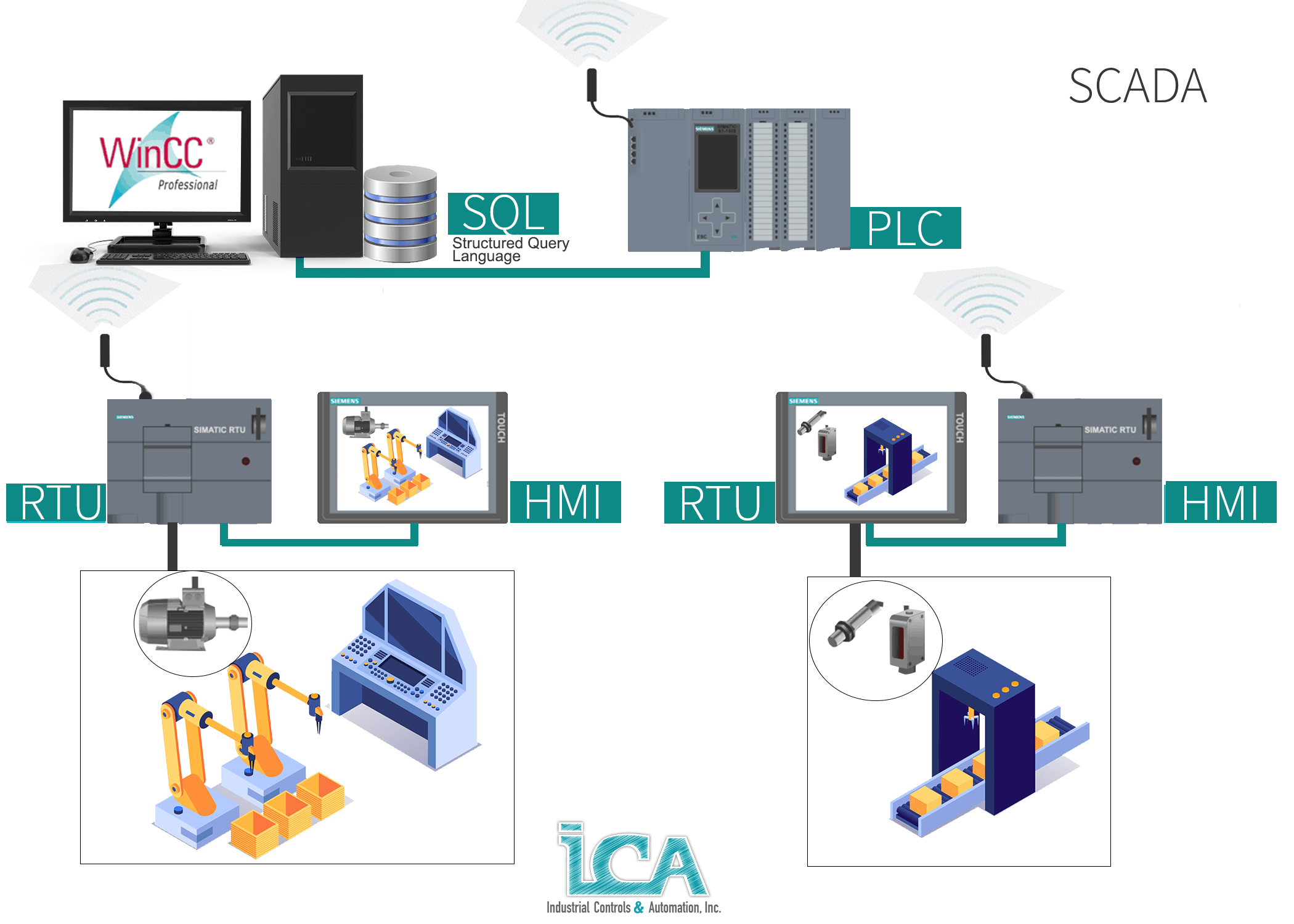
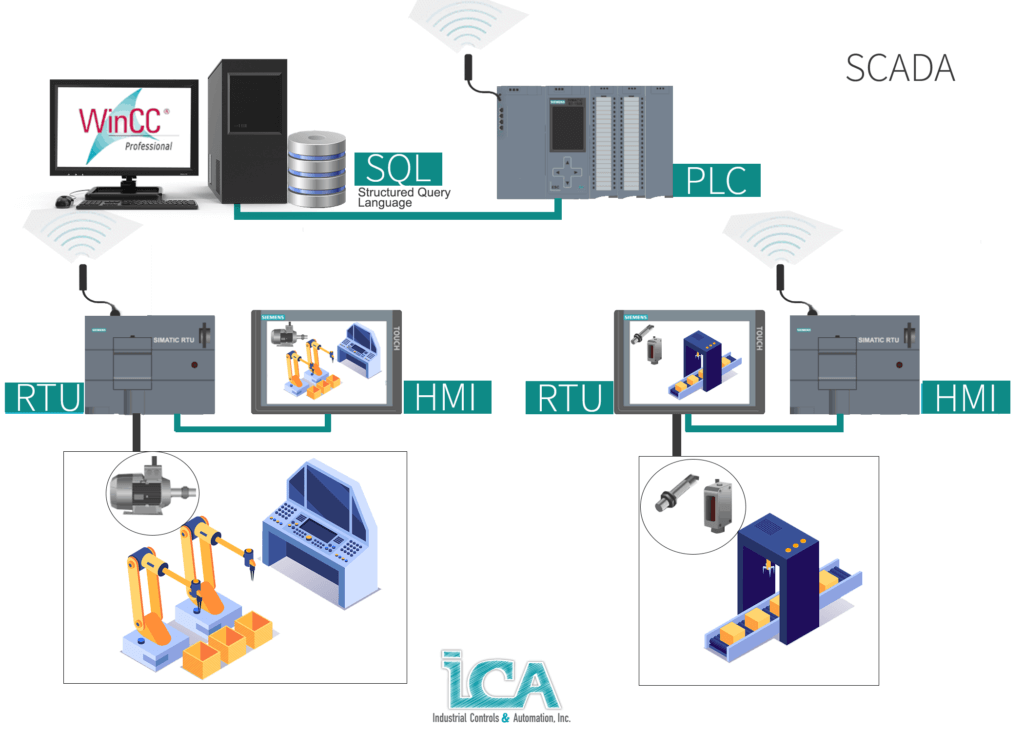
SCADA is a type of software that gathers, quickly analyzes real-time data, and sends commands to control processes. This system is fundamental in the automation industry because it allows businesses to study and anticipate optimal responses automatically. SCADA’s reliable operability and communication are vital to a company’s productivity.
Additionally, SCADA facilitates the control of hardware and makes a record of the data collected from all remote locations. The SCADA software is connected to PLC’s, computers, human–machine interface (HMI), graphical user interfaces, RTU’s (Remote Terminal Unit), sensors, networked data communications, and other devices (depending on the processing plant needs) in order to give a wide picture of the process.
As a central system, it is installed most of the time, in a monitoring hub at a plant. The software works with a wide diversity of other systems, collecting vast amounts of data for evaluation purposes. From this data, the operator can enter the changes needed through the SCADA interface in order to control the operation and flow of the process.
Also, there are four types (generations) of SCADA systems:
- Early SCADA (Monolithic)
- Second Generation: Distributed SCADA Systems
- Third Generation: Networked SCADA systems
- Fourth Generation: Internet of things (IoT technology), SCADA systems.
Common Subject : PLC Vs. SCADA
As mentioned before, SCADA is software, and a PLC (Programable Logic Controller) on the other hand, is a piece of physical hardware. The PLCs need SCADA to control their function, but SCADA depends on data from the PLCs to finish its overview. These technologies are fundamentally partners for an efficient and safe plant operation. In the end, it is not a matter of scada vs. plc, it is simply understanding how they both play an important role for an outstanding performance in the industrial automation world.
What’s Coming?
The growth of the system is vital for supporting society’s growing demand for products, services, and utilities. The future brings many new opportunities for innovation and advancements in SCADA technology. The arrival of 5G will make gathering data easier, but this opens the door to new challenges for SCADA, which will lead to changes and the development of an updated system.
Our engineers at Industrial Controls and Automation have years of knowledge working and programming the SCADA interface and many others; contact us if you ever need any type of programming service.
By Grace Ramirez.
ICA has a team of highly qualified engineers who are in constant training to stay up to date with the latest technology in the industrial automation world. We offer services such as changes & updates of panel/control boards, programing of data acquisition software (scada), field repair, troubleshooting & installation of security systems, programming of plcs & other devices, design aseembly & installation of panel boards for applications without plc. (motor control, lighting, etc.), configuration and systems integration (automation), among many other services. You can find more information about each service in the drop-down menu of the main bar.
If you have a question regarding our services, engineering projects or any other doubts, please contact us!
-
 LC1G500LSEA Contactor High Power Tesys Giga 3 Pole/NO. AC 3 500A 200-500VAC/DC Coil$2,250.00
LC1G500LSEA Contactor High Power Tesys Giga 3 Pole/NO. AC 3 500A 200-500VAC/DC Coil$2,250.00 -
 LC1D09P7 IEC contactor, TeSys Deca, nonreversing, 9A, 3 phase, 3 NO, 230VAC 50/60Hz coil$60.00
LC1D09P7 IEC contactor, TeSys Deca, nonreversing, 9A, 3 phase, 3 NO, 230VAC 50/60Hz coil$60.00 -
 ZLD18-4AB4A2 Photoelectric retro-reflective sensor, Dual lens$65.00
ZLD18-4AB4A2 Photoelectric retro-reflective sensor, Dual lens$65.00 -
 HTE18-F4A2BLA00 Hybrid Photoelectric Sensors SureSense$80.00
HTE18-F4A2BLA00 Hybrid Photoelectric Sensors SureSense$80.00 -
 YG2A25-100UB6XLEAX Female connector, M12, 5-pin, angled, A-coded$60.00
YG2A25-100UB6XLEAX Female connector, M12, 5-pin, angled, A-coded$60.00 -
 YF2A25-100UB6XLEAX Female connector, M12, 5-pin, straight, A-coded$58.00
YF2A25-100UB6XLEAX Female connector, M12, 5-pin, straight, A-coded$58.00 -
 YF2A25-050UB6XLEAX Female connector, M12, 5-pin, straight, A-coded$38.00
YF2A25-050UB6XLEAX Female connector, M12, 5-pin, straight, A-coded$38.00 -
 YG2A14-150VB3XLEAX Female connector, M12, 4-pin, angled, A-coded$23.00
YG2A14-150VB3XLEAX Female connector, M12, 4-pin, angled, A-coded$23.00 -
 YG2A14-100VB3XLEAX Female connector, M12, 4-pin, angled, A-coded$18.00
YG2A14-100VB3XLEAX Female connector, M12, 4-pin, angled, A-coded$18.00